News
Zero Trust Architecture in a Remote World: Securing the New Normal

By Abuh Ibrahim Sani
The ongoing shift to remote work, prompted by the global Covid-19 pandemic, has permanently changed the way organizations and certain government agencies function. What began as a temporary fix for maintaining consistency has transformed into a permanent approach to business for numerous companies. However, the change brings about considerable security obstacles. Traditional network security models, which rely on perimeter-based defenses, are not adequate for a modern environment where employees work remotely from multiple devices. This is how the Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is utilized in the new era of cybersecurity.
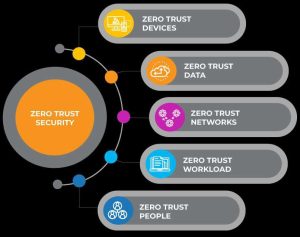
Introducing the Zero Trust Architecture, a strategic shift in cybersecurity that is built on the belief that no entity in the network, regardless of location, should be automatically trusted. This model is especially relevant in situations of remote work where the lines between the company’s network are not clear, making it a great structure for applying Zero Trust. Zero Trust’s fundamental principles of strict verification and limited access privileges create a strong base for protecting remote employees and data from the challenges of cyber threats.
Understanding Zero Trust: “Never Trust, Always Verify”
The foundation of the Zero Trust model is based on a fundamental principle. Do not automatically trust anyone; consider everyone a potential suspect until they can be verified beyond a reasonable doubt, regardless of their location within or outside the network. Zero Trust differs from traditional security models by assuming that potential threats can originate from any source, not just from within the corporate network where users are presumed trustworthy. Each access request is confirmed, approved, and consistently supervised according to user identity, device security state, and request context. Zero trust is not a specific product or technology, but rather a holistic strategy that combines different security principles and tools to verify access strictly and reduce threats by segmenting resources and implementing least-privilege access.
Why Remote Work Demands Zero Trust
The traditional network perimeter has disappeared with remote work. Employees now access company data from their home networks, coffee shops, or shared spaces, often using their own devices. This new version brings about various difficulties in home and public Wifi networks oftens lack enterprise-level security, making remote workers more vulnerable to attacks like man-in-the middle or eavesdropping . The rise of software-as-service(SaaS) and cloud based application has enabled remote work flexibility but complicates oversight. Sensitive corporate data may be accessed and stored outside the traditional network, increasing the attack surface. Employees are no longer restricted to corporate devices. Many use personal devices or BYOD(Bring Your Own Device), which may not have the same security configuration as enterprise-managed systems.
In a remote environment, organization cannot longer rely on internal trust, especially when collaboration spans across teams, contractors, and third-party vendors. Remote workers face a higher likelihood of being preyed upon by phishing attempts and social engineering tactics. In the absence of IT teams physically present and the increased stress of working alone, employees may be more susceptible to sophisticated attacks aimed at stealing credentials and breaching corporate systems. In this landscape, Zero Trust becomes important for securing remote work environments.
Implementing Zero Trust Architecture in a Remote Workforce
Shifting to a Zero Trust model in a remote setting requires a strategic plan that emphasizes thorough identity and device validation, secure access control, education, and continuous monitoring. These measures involve various steps to strengthen the remote work infrastructure against possible cybersecurity risks. The following measures should be considered when adopting remote work environments.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity is the foundation of the Zero Trust approach. Each individual, whether they are a staff member, freelancer, or external supplier, needs to have their identity confirmed. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and biometric verification provides an additional level of security on top of traditional username and password authentication. Furthermore, features such as Single Sign-On (SSO) and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) guarantee that users only have the necessary level of access required for their tasks.
- Principle of Least Privilege (Access Control)
In Zero Trust environments, policies are both dynamic and contextually sensitive. Access is provided by considering contextual factors such as user location, device status, time of access, and the sensitivity of the requested data, instead of giving blanket permissions. This method, commonly referred to as adaptive authentication, guarantees that access restrictions change according to up-to-date information.
- Endpoint Security
Ensuring device security is of utmost importance as employees use a variety of devices to access corporate data. Before permitting access, organizations must assess the security status of every device as part of implementing Zero Trust. This involves implementing patch management, malware detection, and configuration policies on all devices. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools continuously monitor device behavior, detect anomalies, and promptly respond to threats.
- Micro-Segmentation
Zero Trust Architecture focuses on limiting access to only those resources necessary for a user’s job. Through micro-segmentation, networks are divided into smaller, isolated zones, each with its own security policies. Even if a cybercriminal gains access to one segment, they won’t have unrestricted access to other areas of the network. This significantly reduces the blast radius in case of an attack.
- Continuous Monitoring and Analytics
Verification is not a singular event in a Zero Trust framework. Constant monitoring of network traffic, endpoints, and user behaviours is essential for organizations to detect potential threats. SIEM and UEBA systems are capable of identifying irregularities like unusual login locations, unexpected data transfers, or unusual activity patterns, which could suggest malicious behaviour.
- Data Encryption and Protection
Encryption is essential in Zero Trust due to the transmission of data through insecure networks and endpoints. Data needs to be encrypted while in motion and while at rest, guaranteeing that hackers are unable to steal sensitive information even if they intercept data transmission or breach devices. DLP tools at endpoints can aid in enforcing policies to stop unauthorized sharing of vital information.
- Securing all resources
In a Zero Trust setting, all assets are safeguarded equally, whether they are in the cloud, on-site, or spread across diverse hybrid systems. This includes securing cloud apps and data with the same level of protection as on-site resources, defending older systems lacking contemporary security measures, and ensuring that all devices, workloads, APIs, and communication channels undergo consistent security evaluation, establishing a cohesive and safe environment.
- Educate and Train the Employees
A knowledgeable and alert staff is essential for Zero Trust security. It is crucial to have regular security training sessions on phishing awareness, security best practices, and the importance of security in remote work environments. Implementing the Zero Trust model during remote work allows organizations to establish a secure setting that can effectively address the unique challenges of working remotely. This thorough method guarantees that the integrity and security of the organization’s data and resources are upheld no matter where employees are working, in line with the zero Trust principles of not inherently trusting any entity in or out of the network.
Benefits of Zero Trust for Remote Work
Traditional security models are no longer sufficient due to the rapid evolution of cyber threats and the growing complexity of modern work environments. Securing corporate assets requires a new approach as businesses shift to cloud-based services, facilitate remote work, and incorporate various devices into their networks. This is when the adoption of a Zero Trust approach becomes essential.
Zero Trust mitigates the risk of data breaches by continuously verifying every access attempt and reducing the exposure of critical resources. Zero Trust allows for a secure and smooth remote work experience by separating security from a specific location or device. Workers have the flexibility to work remotely, as long as the company upholds strict security measures. As Zero Trust does not depend on trust within the internal network, it reduces the danger of disgruntled employees or compromised accounts.
Many industries are subject to strict data privacy and security regulations. Zero Trust aids compliance by ensuring that data access is limited, monitored, and secure. As companies increasingly use cloud services, remote employees, and dispersed teams, Zero Trust ensures security grows in line with advancements. It is a method designed to be flexible, allowing organizations to adjust to emerging threats and technologies.
Implementation Challenges And Considerations
Even though the advantages of Zero Trust are evident, the implementation of this structure necessitates meticulous planning and financial resources. Zero Trust signifies a major shift from conventional security methods. Organizations need to make sure that employees, especially those working in IT, are knowledgeable about the new approach. Building a Zero Trust Architecture requires a substantial investment in technology, training, and process transformation due to its cost and complexity. Yet, the advantages in the long run are usually more significant than these expenses. Many businesses depend on older systems that may not smoothly integrate with a Zero Trust model. It is advised to begin with the most essential systems when gradually implementing changes.
Conclusion
With remote work becoming increasingly common, organizations require a security model that can adjust to the unique challenges presented in this new setting. The Zero Trust Architecture offers the structure to protect a geographically dispersed workforce by verifying all access requests, monitoring every device, and safeguarding every resource. In a changing world of evolving threats and remote work, Zero Trust is not just an option—it is crucial.
Implementing zero trust in remote work settings includes utilizing multifactor authentication, biometric verification using secure, encrypted connections like VPNs, and consistently monitoring and assessing user and device actions for possible risks. Adopting Zero Trust principles aligns with remote work security needs and provides a thorough structure for organizations aiming to effectively secure their remote employees. By following Zero Trust principles, businesses can establish a security stance that is flexible, robust, and equipped to tackle the specific obstacles brought on by remote work. Focusing on Zero Trust is a pre-emptive measure to guarantee that the security measures adapt as the workplace changes.
Headlines
Noble Ladies Champion Women’s Financial Independence at Grand Inauguration in Abuja
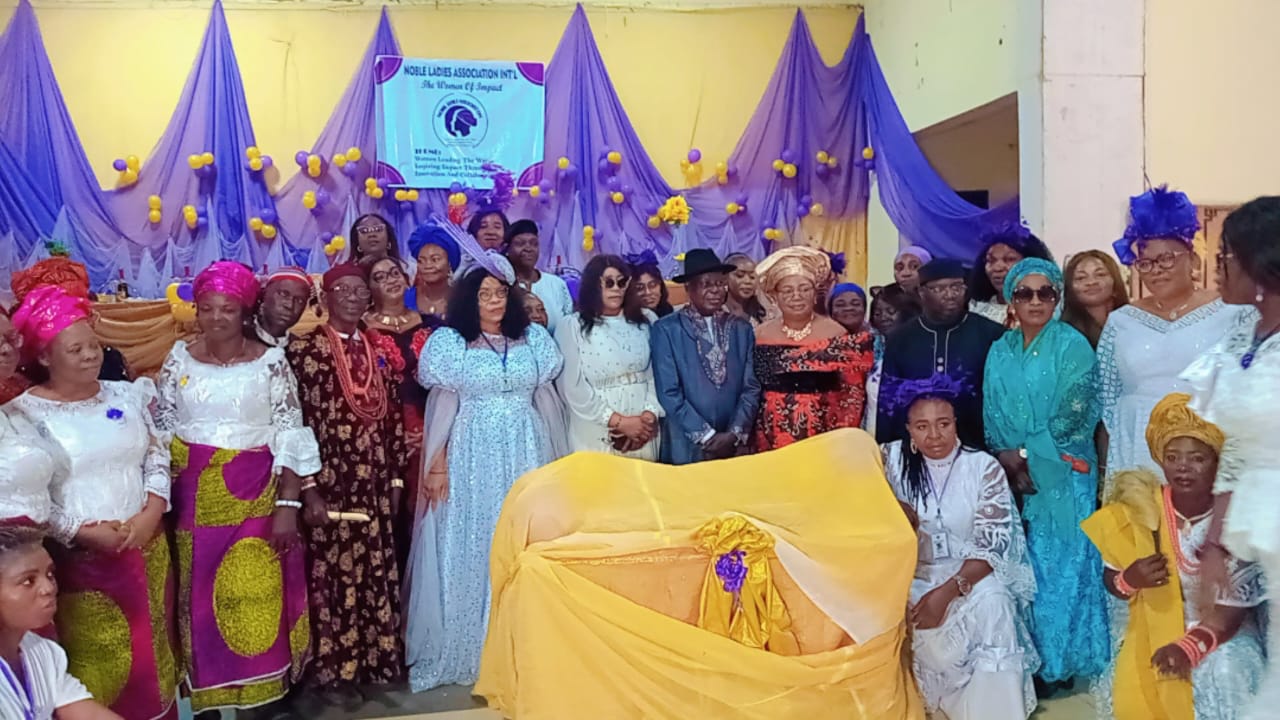

Women from diverse backgrounds across Nigeria and beyond gathered at the Art and Culture Auditorium, Abuja, for the inauguration and convention of the Noble Ladies Association. The event, led by the association’s Founder and “visionary and polished Queen Mother,” Mrs. Margaret Chigozie Mkpuma, was a colourful display of feminine elegance, empowerment, and ambition.
The highly anticipated gathering, attended by over 700 members and counting, reflected the association’s mission to help women realise their potential while shifting mindsets away from dependency and over-glamorization of the ‘white collar job.’ According to the group, progress can be better achieved through innovation and creativity. “When a woman is able to earn and blossom on her own she has no reason to look at herself as a second fiddle,” the association stated.
One of the association’s standout initiatives is its women-only investment platform, which currently offers a minimum entry of ₦100,000 with a return of ₦130,000 over 30 days—an interest rate of 30 percent. Some members invest as much as ₦1 million, enjoying the same return rate. Mrs. Mkpuma explained that the scheme focuses on women because “women bear the greater brunt of poverty” and the platform seeks “to offer equity in the absence of economic equality.”
Education is also central to the Noble Ladies’ mission, regardless of age. Their mantra, “start again from where you stopped,” encourages women to return to school or upgrade their skills at any stage in life. The association believes that financial stability is vital in protecting women from cultural practices that dispossess widows of their late husbands’ assets, while also enabling them to raise morally and socially grounded families.
Founded on the vision of enhancing women’s skills and achieving financial stability, the association rests on a value system that discourages pity and promotes purpose. “You have a purpose and you build on that purpose to achieve great potentials and emancipation,” Mrs. Mkpuma said.
A criminologist by training and entrepreneur by practice, she cautions against idleness while waiting for formal employment. “There are billions in the informal and non-formal sectors waiting to be made,” she said, rejecting the “new normal of begging” and urging people to “be more introspective to find their purpose in life and hold on to it.”
Mrs. Mkpuma’s management style keeps members actively engaged, focusing on vocational skills and training to prepare them for competitive markets. She is exploring “innovative integration of uncommon technologies” and is already in talks with international franchises to invest in Nigeria, with Noble Ladies as first beneficiaries.
The association’s core values include mutual respect, innovation, forward-thinking, equal opportunity, and financial emancipation. With plans underway to establish a secretariat in the heart of Abuja, the group aims to expand its impact.
The event drew high-profile guests, including former Inspector General of Police, Mike Okiro, and a host of VIPs, marking a significant milestone in the association’s drive for women’s empowerment.
Headlines
NEPZA, FCT agree to create world-class FTZ environment
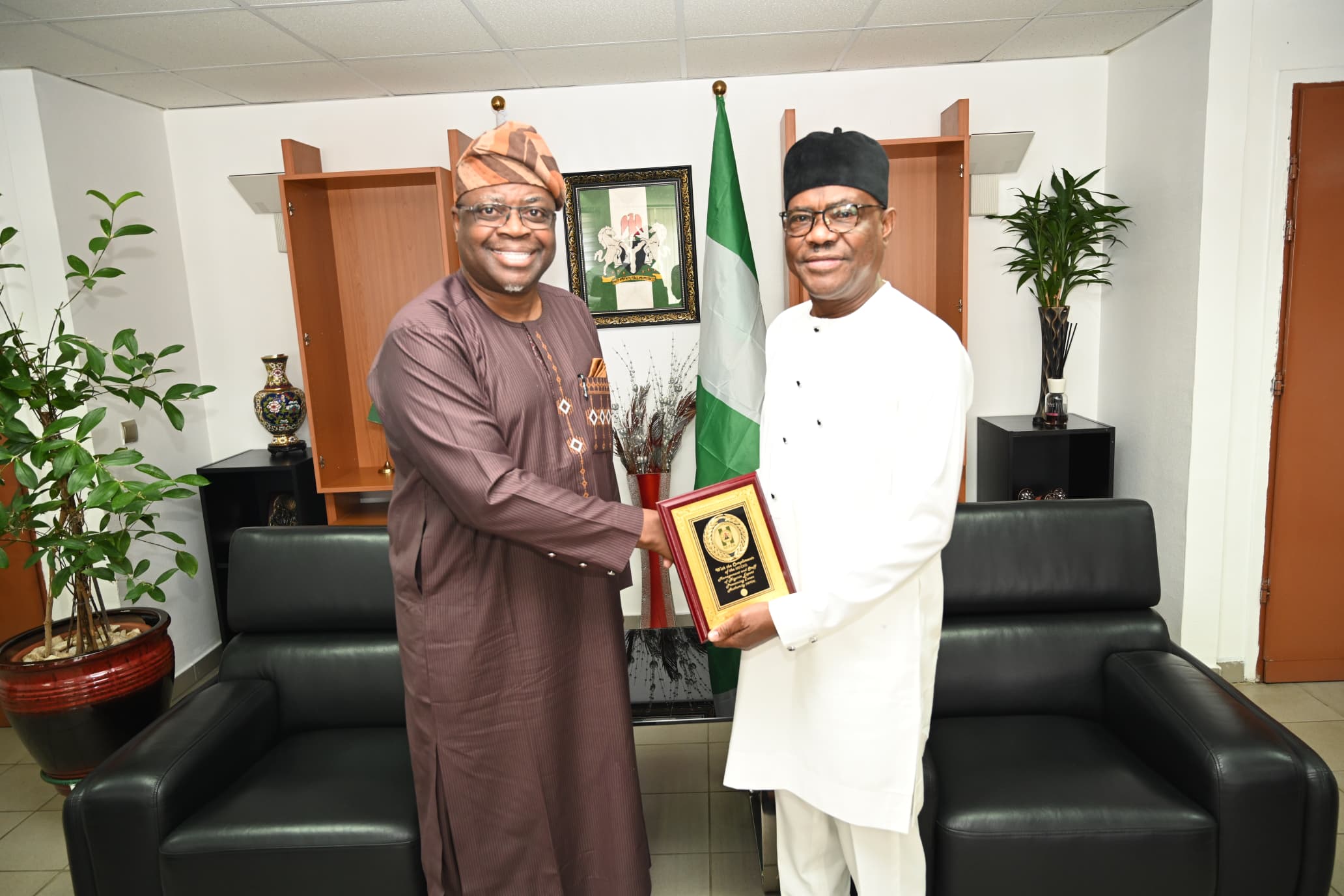

The Nigeria Export Processing Zones Authority (NEPZA) has stepped in to resolve the dispute between the Federal Capital Territory Administration and the Abuja Technology Village (ATV), a licensed Free Trade Zone, over the potential revocation of the zone’s land title.
Dr. Olufemi Ogunyemi, the Managing Director of NEPZA, urged ATV operators and investors to withdraw the lawsuit filed against the FCT administration immediately to facilitate a roundtable negotiation.
Dr. Ogunyemi delivered the charge during a courtesy visit to the Minister of the Federal Capital Territory, Barrister Nyesom Wike, on Thursday in Abuja.
You will recall that the ATV operators responded to the revocation notice issued by the FCT administration with a lawsuit.
Dr. Ogunyemi stated that the continued support for the growth of the Free Trade Zones Scheme would benefit the nation’s economy and the FCT’s development, emphasizing that the FCT administration recognized the scheme’s potential to accelerate industrialisation.
Dr. Ogunyemi, also the Chief Executive Officer of NEPZA, expressed his delight at the steps taken by the FCT minister to expand the economic frontier of the FCT through the proposed Abuja City Walk (ACW) project.
Dr. Ogunyemi further explained that the Authority was preparing to assess all the 63 licensed Free Trade Zones across the country with the view to vetting their functionality and contributions to the nation’s Foreign Direct Investment and export drives.
“I have come to discuss with His Excellency, the Minister of the Federal Capital Territory on the importance of supporting the ATV to succeed while also promoting the development of the Abuja City Walk project. We must work together to achieve this for the good of our nation,” he said.
On his part, the FCT Minister reiterated his unflinching determination to work towards President Bola Ahmed Tinubu’s Renewed Hope Agenda by bringing FDI to the FCT.
“We must fulfil Mr. President’s promises regarding industrialization, trade, and investment. In this context, the FCT will collaborate with NEPZA to review the future of ATV, a zone that was sponsored and supported by the FCT administration,” Wike said.
Barrister Wike also said that efforts were underway to fast-track the industrialisation process of the territory with the construction of the Abuja City Walk.
The minister further said the Abuja City Walk project was planned to cover over 200 hectares in the Abuja Technology Village corridor along Airport Road.
According to him, the business ecosystem aimed to create a lively, mixed-use urban center with residential, commercial, retail, hospitality, medical, and institutional facilities.
He added that the ACW would turn out to be a high-definition and world-class project that would give this administration’s Renewed Hope Agenda true meaning in the North-Central Region of the country.
Barrister Wike also indicated his continued pursuit of land and property owners who failed to fulfil their obligations to the FCT in his determination to develop the territory.
Headlines
Benue IDPs block highway, demand return to ancestral homes
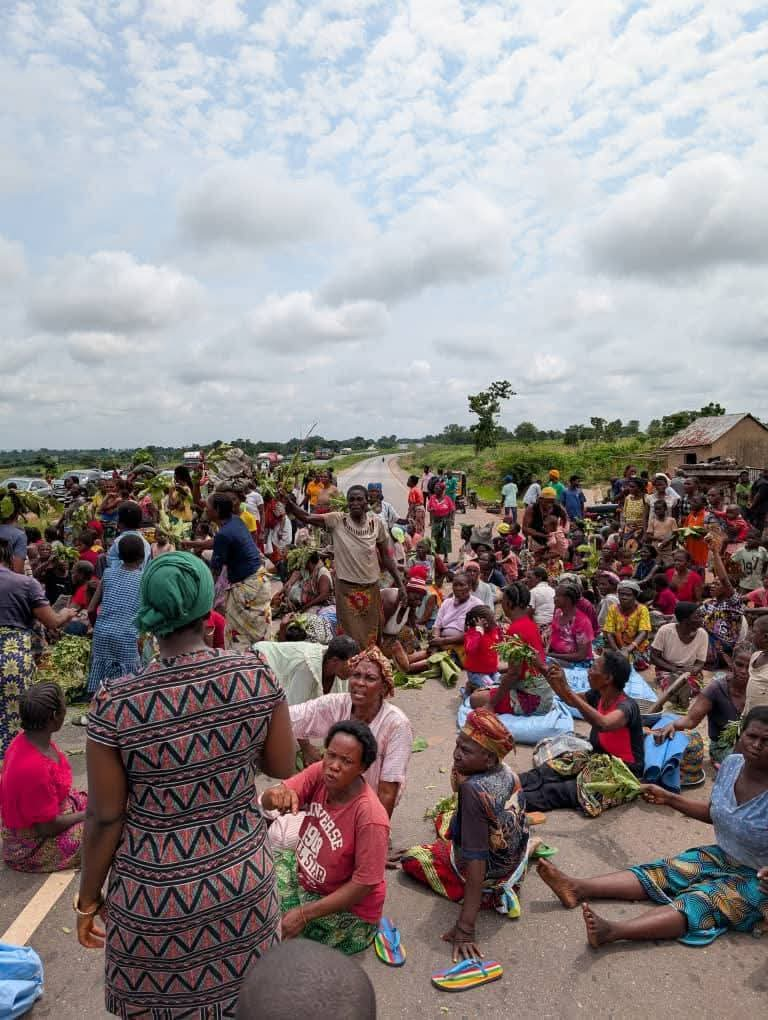

Vehicular movement along the Yelwata axis of the Benue–Nasarawa highway was brought to a standstill on Wednesday as Internally Displaced Persons, IDPs, staged a protest, demanding immediate return to their ancestral homes.
The protesters, believed to be victims of persistent attacks by suspected herdsmen, blocked both lanes of the busy highway for several hours, chanting “We want to go back home”.
The protest caused disruption, leaving hundreds of motorists and passengers stranded.
Eyewitnesses said the displaced persons, many of whom have spent years in overcrowded IDP camps, are expressing deep frustration over the government’s delay in restoring security to their communities.
“We have suffered enough. We want to return to our homes and farms,” one of the protesters told reporters at the scene.
Security personnel were reportedly deployed to monitor the situation and prevent any escalation, though tensions remained high as of press time.
Efforts to reach the Benue State Emergency Management Agency, SEMA, and other relevant authorities for comment were unsuccessful.
-

 Headlines4 years ago
Headlines4 years agoFacebook, Instagram Temporarily Allow Posts on Ukraine War Calling for Violence Against Invading Russians or Putin’s Death
-
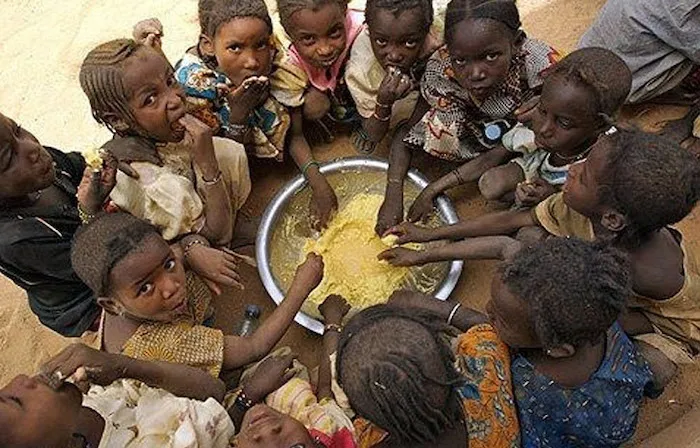

 Headlines4 years ago
Headlines4 years agoNigeria, Other West African Countries Facing Worst Food Crisis in 10 Years, Aid Groups Say
-

 Foreign3 years ago
Foreign3 years agoNew York Consulate installs machines for 10-year passport
-
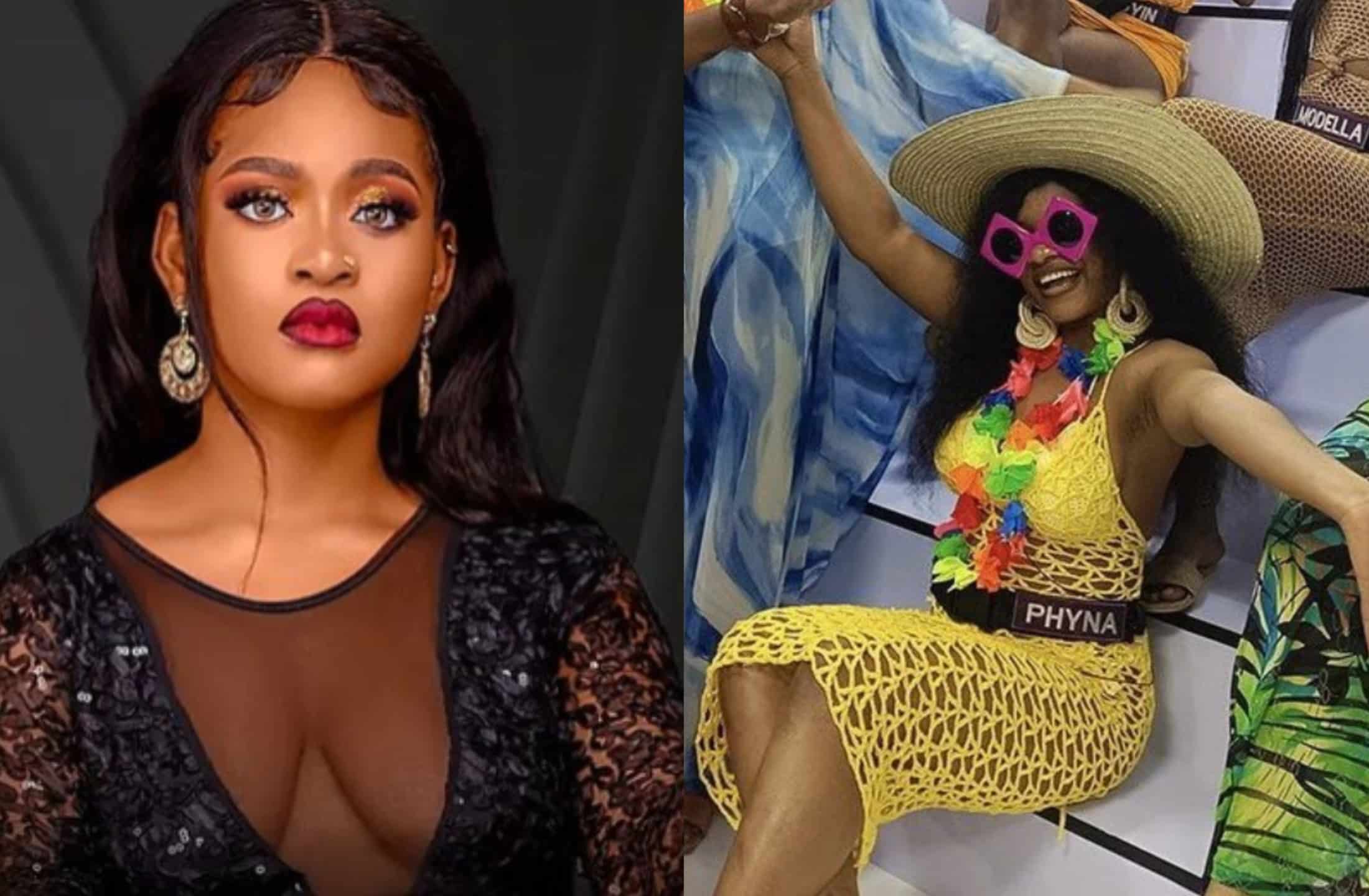

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoPhyna emerges winner of Big Brother Naija Season 7
-
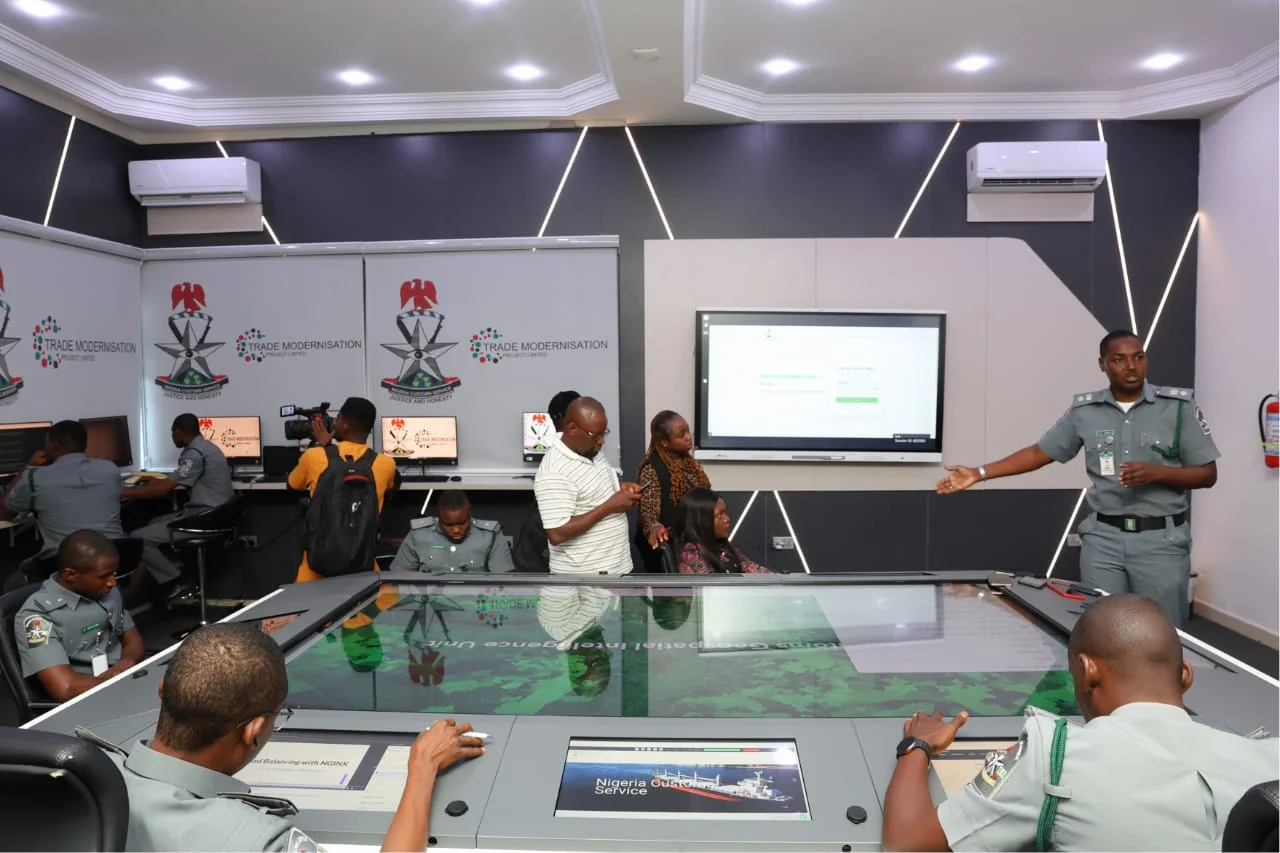

 Headlines1 year ago
Headlines1 year agoNigeria Customs modernisation project to check extortion of traders
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoMovie download platform, Netnaija, announces closure
-

 Economy2 years ago
Economy2 years agoWe generated N30.2 bn revenue in three months – Kano NCS Comptroller
-

 Headlines1 year ago
Headlines1 year agoPhilippines’ Vice President Sara Duterte resigns from Cabinet







