Health
Hepatitis kills 124,000 Africans annually – WHO
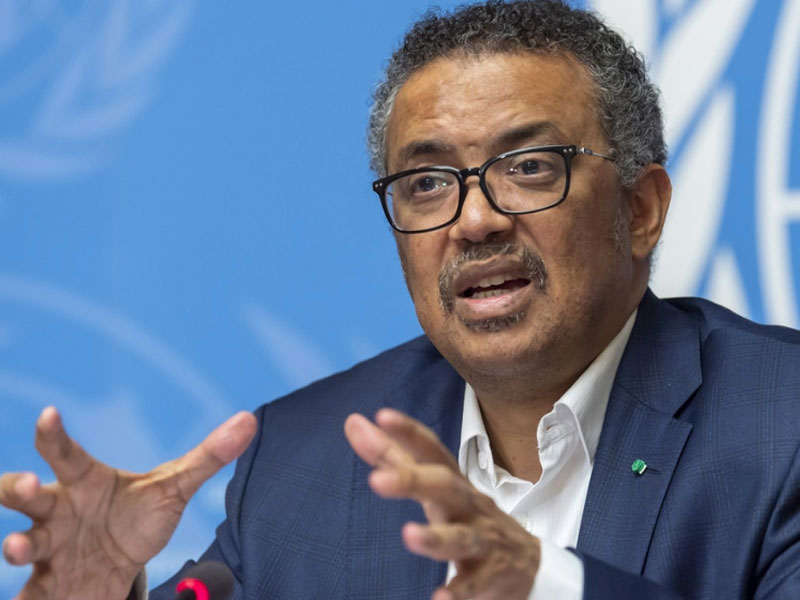

The World Health Organisation, WHO, has revealed that more than 124,000 Africans die every year from the consequences of undetected and untreated hepatitis.
The WHO’s Regional Director for Africa, Matshidiso Moeti, disclosed this in her statement to mark this year’s World Hepatitis Day.
World Hepatitis Day is marked on 28 July every year. The theme of this year’s commemoration is ‘hepatitis can’t wait’.
Ms Moeti, according to Daily Trust, said hepatitis is a silent epidemic in Africa, adding that more than 90 million people are living with hepatitis in the region, this accounts for 26% of the global total.
She said: “Around 4.5 million African children under five years old are infected with chronic hepatitis B, reflecting an enormous 70% of the global burden in this age group.
“The global target of less than 1% incidence of hepatitis B in children under five years has been reached, but the African Region is lagging behind at 2.5%.
“Most of these cases could be prevented by eliminating mother-to-child transmission of the disease, during or shortly after birth and in early childhood.
“Key interventions against hepatitis B include vaccination at birth and in early childhood, screening pregnant women, and providing timely treatment.”
While calling on all countries to rapidly improve access to services to prevent, diagnose and treat hepatitis, Ms Moeti also enjoined countries to integrate the Hepatitis B Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission, PMTCT, in the ante-natal care package together with the HIV and Syphilis PMTCT program.
She said only 14 countries in the region were implementing hepatitis B birth-dose vaccine.
According to her, among people who are infected, nine out of 10 have never been tested because of limited awareness and access to testing and treatment.
“Even among countries offering hepatitis B birth-dose vaccine, health systems are facing challenges in ensuring pregnant women and mothers are tested and that those who test positive are treated,” she said.
The WHO regional boss added that there were many promising developments on hepatitis.
She said these include the launch of the first global strategy on hepatitis in 2016, along with increased advocacy in recent years, and “political will is starting to translate into action and Hepatitis medicines become much more affordable.”
She said African leaders had committed to address viral hepatitis as a public health threat in the Cairo Declaration in February 2020 and to guide action on hepatitis.
Also, 28 African countries now have strategic plans in place, and at the global level, WHO guidelines were launched last year on the prevention of mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B.
Health
First Lady directs establishment of PHC in Sauka FCT to combat TB
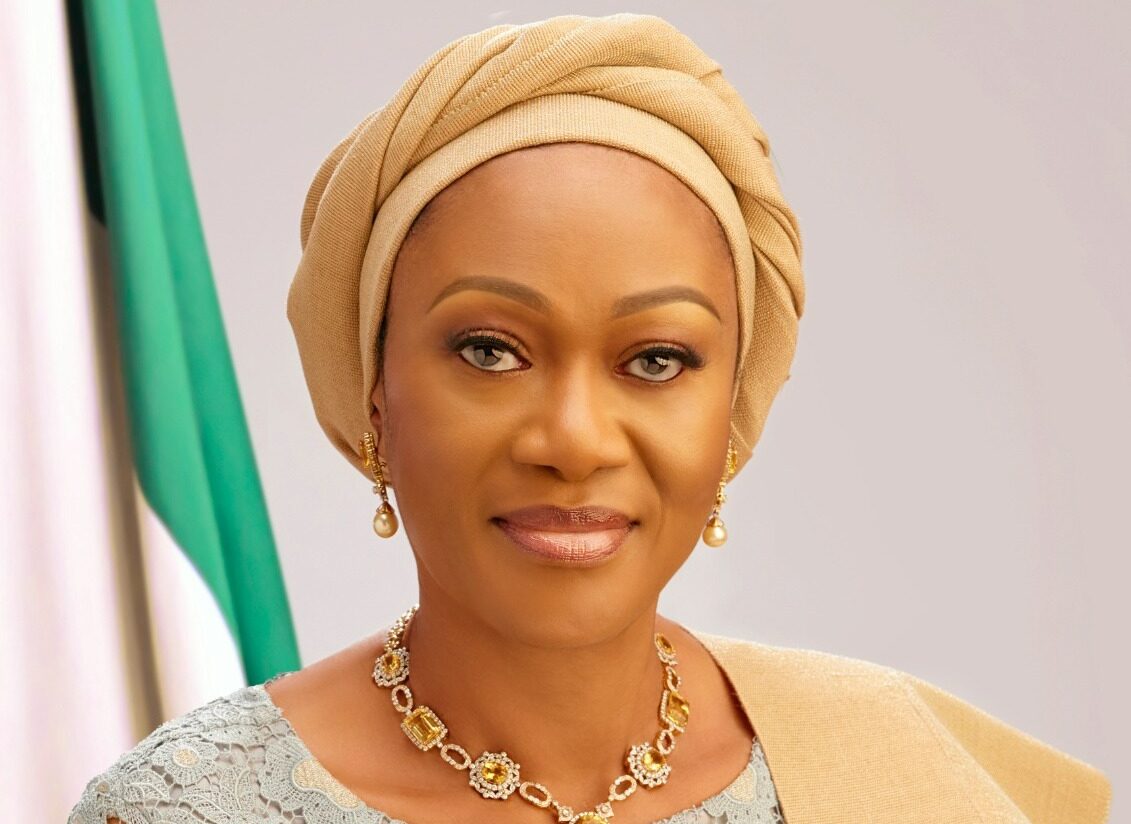

The First Lady of Nigeria, Mrs Oluremi Tinubu, has directed Dr Adedolapo Fasawe, Mandate Secretary of the FCT Health Services and Environment Secretariat, to oversee the establishment of a Primary Healthcare Centre in Sauka, FCT.
A statement issued by the Special Adviser to the Secretary, Bola Ajao, on Wednesday highlighted that the initiative aimed to strengthen healthcare services in the region.
It also emphasised the goal of combating tuberculosis (TB), with support from FCT Minister, Mr Nyesom Wike.
According to the statement, Mrs Tinubu, who also serves as the Global and National Stop TB Champion, made the announcement at an event in Sauka, FCT, to commemorate World Tuberculosis Day 2025.
The event was organised by the Federal Ministry of Health in collaboration with the FCT Health Services Secretariat, Stop TB Partnership Nigeria, the World Health Organisation (WHO), and other partners.
During her speech, the First Lady emphasised the importance of grassroots interventions in the fight against TB.
She noted that the event themed, “Yes! We Can End TB: Commit, Invest, Deliver,” had been locally translated to “We Fit Run Am; A Collective Call for Action Against TB” to better resonate with the community.
“To support the fight against this communicable disease, I will not only donate N1 billion but also approve the establishment of a Primary Healthcare Centre in Sauka Community.
“This initiative aligns with President Tinubu’s Renewed Hope Agenda for an efficient healthcare system,” the First lady stated.
The First Lady added that Fasawe would oversee the project’s implementation with the backing of the dedicated FCT Minister, Wike.
She further explained that the new facility would serve as a critical hub for TB detection, treatment, and general healthcare services, ensuring that residents received timely and quality medical care.
In spite of TB being preventable and treatable, the First Lady pointed out that it remained a significant public health challenge in Nigeria, which ranked among the countries with the highest TB burden globally.
“This underscores the urgent need for improved healthcare services and stronger community-based interventions.”
In her response, Fasawe commended the First Lady for her unwavering dedication and strong support in the fight against TB elimination.
She also acknowledged the efforts of FCT healthcare workers, whose hard work had contributed to significant improvements in the health system.
“The establishment of the new Primary Healthcare Centre in Sauka is a significant step toward enhancing healthcare services, improving TB control, and ensuring accessible healthcare for all in the FCT,” Fasawe affirmed.
The event also featured an exhibition stand by the Public Health Department of the FCT, where attendees were provided with free TB testing.
Key stakeholders in attendance included Hajiya Nana Shettima, Wife of the Vice President; Members of the National Assembly; Dr Iziaq Salako, Minister of State for Health; and Mrs Adekemi Nanpad, Comptroller General of the Nigeria Immigration Service.
Also present were wives of the Federal Executive Council members, Dr Walter Kazadi Mulombo, WHO Country Representative, and many others.
Health
Kano Govt pledges quality healthcare in custodial centres
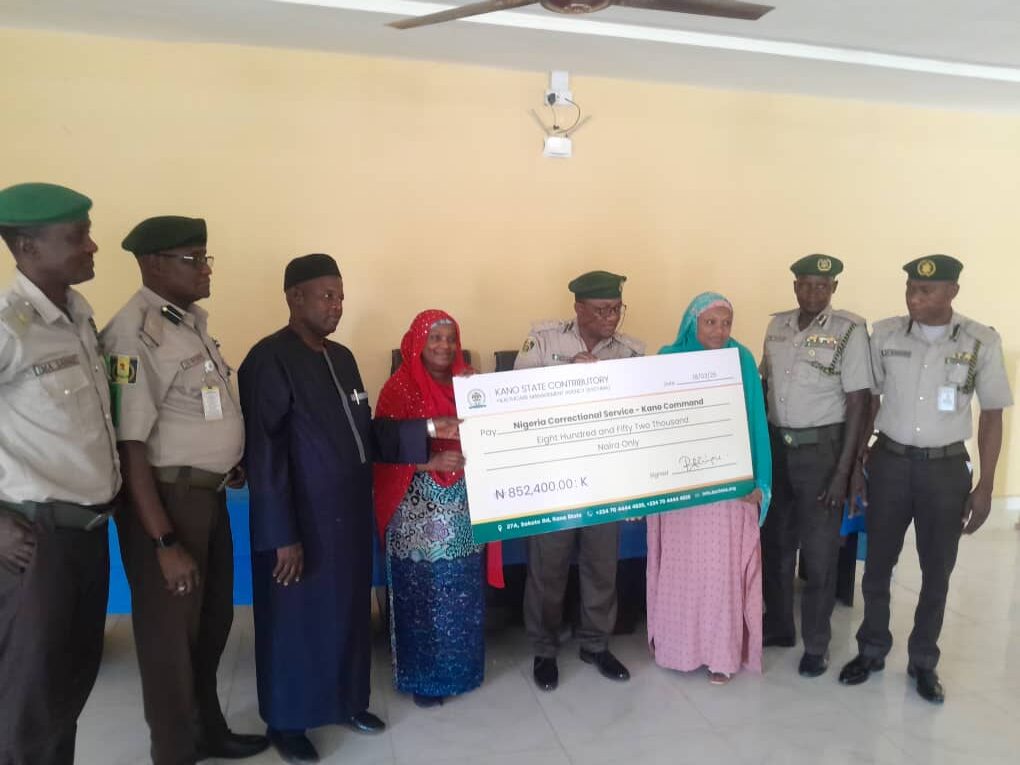
The Kano State Government has pledged its commitment to quality healthcare services for inmates in custodial centres across the state.
The Executive Secretary of the Kano State Contributory Healthcare Management Agency (KSCHMA), Dr Rahila Aliyu-Mukhtar, made the pledge while presenting the allocation of a monthly capitation of N852, 400 to support medical services for inmates in custodial centres.
She lauded Gov. Abba Kabir-Yusuf, for supporting vulnerable individuals and prioritising healthcare for inmates.
The executive secretary also commended the Kano command of the Nigerian Correctional Service for its support and cooperation.
She commended Kano for being one of the first states to enrol inmates in a structured healthcare scheme.
Responding, the Controller of Corrections, Kano State Command, Ado Inuwa expressed appreciation to the state government for its unwavering support in the enrollment of inmates under the healthcare services scheme.
He assured that the allocated funds would be utilised judiciously to cover essential medical treatments and emergency care for inmates.
Inuwa lauded Aliyu-Mukhtar for her zeal, determination and commitment to humanity, particularly in ensuring that inmates have access to healthcare services.
NAN reports that on Dec. 31, 2024, the state government approved the enrolment of inmates in custodial facilities into the State’s Health Contributory Scheme, ensuring they now enjoy health insurance coverage.The scheme provides inmates with access to basic and comprehensive healthcare services while in custody.
Headlines
NAFDAC strengthens regulations to combat antimicrobial resistance in Nigeria

The National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control (NAFDAC) has intensified its efforts to combat Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) in Nigeria by implementing stricter regulations and surveillance measures.
Dr Tunde Sigbeku, Deputy Director and AMR-OH Focal Person at NAFDAC, said this on Thursday in Lagos.
Sigbeku spoke during a five-day training session for journalists, civil society organisations (CSOs) and community-based organisations (CBOs) focused on AMR.
The News Agency of Nigeria (NAN), reports that the training was organised by the Fleming Fund Country Grant (FFCG II).
The project is supported by the UK Government’s Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO).
Sigbeku highlighted the dangers of AMR, emphasising that it poses a severe threat to human, animal, and environmental health.
He said that NAFDAC had implemented several policies, including banning the use of antibiotics as growth promoters in livestock and fish production.
“AMR is real and with us in Nigeria. We have cases in hospitals, including babies born with colistin resistance, and it is also present on farms.
“We are taking steps like prohibiting the sale of branded medicated feed in open markets.
We are also restricting the use of certain veterinary drugs in food-producing animals, such as Carbadox, Nitrofural, and Olaquindox.
“We are strengthening port inspections to detect substandard and falsified antibiotics using advanced technologies like TRUSCAN and the Mobile Authentication Service (MAS),” he said l.
According to him, recognising that AMR requires a multi-sectoral approach.
He said that the agency had established collaborations with international and national stakeholders.
He listed such stakeholders to include the World Health Organisation (WHO), the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), and the Fleming Fund.
“NAFDAC is also monitoring the importation and use of human and veterinary antibiotics to ensure compliance with national regulations,” he said.
Sigbeku stressed the need for continuous public awareness and collaboration with research institutions.
“We must educate, advocate, and act now.
“Increased surveillance, research, and policy enforcement are crucial to preventing a post-antibiotic era where common infections become deadly,” he said.
As Nigeria joins the global fight against AMR, he urged healthcare providers, farmers, and the general public to use antibiotics responsibly to preserve their effectiveness for future generations.
NAN recalls that the FFCG II has been instrumental in Nigeria’s fight against AMR.
Managed by Management Sciences for Health (MSH), the project collaborates with the One Health Ministries.
They are the Federal Ministry of Health and the Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Food Security (FMAFS), as well as the Federal Ministry of Environment.
The aim is to implement a coordinated, multisectoral approach addressing AMR across human, animal, and environmental health.
Aligned with Nigeria’s FFCG Phase 2 Country Investment Strategy (CIS), the project focuses on four priority areas:
Producing quality AMR data, analysing data effectively, sharing analysis with decision-makers and promoting sustainable investment to counter AMR.
Through these efforts, the project plays a crucial role in strengthening Nigeria’s response to AMR, a growing public health concern.
-

 Headlines4 years ago
Headlines4 years agoFacebook, Instagram Temporarily Allow Posts on Ukraine War Calling for Violence Against Invading Russians or Putin’s Death
-

 Headlines4 years ago
Headlines4 years agoNigeria, Other West African Countries Facing Worst Food Crisis in 10 Years, Aid Groups Say
-

 Foreign4 years ago
Foreign4 years agoNew York Consulate installs machines for 10-year passport
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoZero Trust Architecture in a Remote World: Securing the New Normal
-

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoPhyna emerges winner of Big Brother Naija Season 7
-

 Headlines1 year ago
Headlines1 year agoNigeria Customs modernisation project to check extortion of traders
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoMovie download platform, Netnaija, announces closure
-

 Economy2 years ago
Economy2 years agoWe generated N30.2 bn revenue in three months – Kano NCS Comptroller







