Africa
High rejection rates for African students battling for Canada visas

Long viewed as a multicultural and inclusive nation, Canada admitted recently that its immigration system is tinged with racism and concern has risen over high rejection rates for African students.
“I have met people who have had their visas refused more than five times,” even though they had been accepted by Canadian universities, says Serge Nouemssi, white coat and pipette in hand.
Originally from Cameroon, the 33-year-old biology student has been working on his doctorate for more than three years in a laboratory at the University of Quebec at Trois-Rivieres (UQTR).
Surrounded by greenery, the campus located halfway between Montreal and Quebec City hosts almost 15,000 students, including the largest proportion of Africans in the province — 65 percent of international students.
READ ALSO: Portugal host Nigeria Today in Lisbon
But “we have seen rejections of up to 80 percent of applicants coming from Africa,” says the school’s rector, Christian Blanchette, who noted it has been an ongoing problem “for several years.”
In a report quietly released at the end of September, the national immigration department said it “recognizes the presence of racism in Canada and within our own organization.”
According to federal data, Quebec is the Canadian province with the highest rejection rate of African students — around 70 percent from French-speaking African nations between 2017 and 2021.
The data says applications from France, Britain or Germany to study in Quebec are almost always accepted — approximately a 90 percent approval rate.
– ‘Absurd’ refusals –
As well as having to pay tuition ranging on average from Can$17,000 (US$12,750) to Can$19,000 per academic year to study in Quebec and rising up to Can$50,000, African students must also provide financial guarantees.
“For us Africans, generally they (immigration officials) insist on proof of financial means” to be able to afford to live and study in Canada, explains Nouemssi.
“There are cases where we have demonstrated financial resources that were close to one million dollars,” explains Caroline Turcotte-Brule, an immigration lawyer. “The agent replied that our client did not have enough financial resources.”
“I have the impression that it’s a bit random,” she adds, specifying that the reason for refusal is often the same: “a fear that the person will not return to his country of origin after” his studies.
“It’s a bit of hypocrisy,” said Krishna Gagne, another lawyer who notes that students have the legal right to consider staying in Canada after their studies.
Ottawa has even been encouraging foreign students to do so as it rolled out incentives in recent months in order to help deal with a labour shortage.
Sitting at her desk in a small laboratory at the end of a maze of underground corridors, Imene Fahmi says that she had to try twice before being able to come and study in Quebec.
“I encountered a lot of difficulties”, explains the Algerian-born doctor, who was refused the first time because the program she’d chosen was “not related to her previous studies,” even though she had been aggressively recruited by her future research director.
She had to apply a second time and wait eight months before finally getting approval.
“In regards to immigration, there doesn’t seem to be an understanding of the nuances and backgrounds of certain students, so we have refusals which are a bit absurd,” her research supervisor Mathieu Piche says, unable to hide his frustrations.
Refusals and delays have consequences on the students but also “on the work of the teachers,” he adds.
– ‘Systemic racism’? –
The problem does not only affect students. In July, Canada faced a backlash over its denials of visas for hundreds of delegates, including Africans, that were to attend the AIDS 2022 conference in Montreal.
In its September report, the government promised better training for its immigration agents, considering creating an ombudsman post to manage disputes and review its much-maligned case processing software.
Those efforts are welcomed by Turcotte-Brule, but she underscores that there has been “a problem of systemic racism for a long time” in Canada and that “it will not be resolved overnight.”
Africa
When the Gatekeeper Fumbles: JAMB’s Error and the Future of Our Youth

When the Gatekeeper Fumbles: JAMB’s Error and the Future of Our Youth
By Matthew Eloyi
It is not every day that a public official publicly sheds tears. And so, when the Registrar of the Joint Admissions and Matriculation Board (JAMB), Professor Ishaq Oloyede, broke down while admitting to errors in the conduct of the 2025 Unified Tertiary Matriculation Examination (UTME), it was a deeply emotional moment. But make no mistake: while the tears may have reflected remorse, they cannot wash away the consequences of what is, quite frankly, a systemic failure.
Let us be clear — JAMB is not merely an examination body. It is a gatekeeper to higher education in Nigeria. It is the bridge between dreams and their realisation for millions of young Nigerians. To fumble that responsibility is not a technical error; it is a breach of trust with life-altering consequences.
With nearly 380,000 candidates now required to retake the exam due to technical glitches and irregularities, one cannot help but ask: How did we get here? And more importantly, why does this keep happening?
For years, JAMB has marketed its transition to computer-based testing as a step toward modernisation. Yet each year seems to expose new cracks in its implementation — from faulty computer systems and power outages to incomplete biometric verification and poorly configured questions. These are not unforeseeable anomalies. They are predictable outcomes of poor planning, lack of oversight, and inadequate investment in infrastructure.
Imagine the psychological toll on the students, many of whom studied day and night, only to be met with malfunctioning systems and flawed questions. Some walked out of examination halls in tears, their confidence shattered, their futures placed in limbo. For those in remote or under-resourced areas, the technical errors are compounded by infrastructural and economic disadvantages. What we are witnessing is not just an exam failure; it is an institutional failure that amplifies inequality.
JAMB’s decision to allow affected candidates a resit is necessary, but it is insufficient. What about those who may never realize they were victims of the glitch? What about those whose faith in the process has been irreparably broken?
Professor Oloyede’s tears may have been sincere, but what Nigerian students need now is not emotion — it is accountability. Heads must roll, systems must be overhauled, and the entire structure must be audited. We cannot allow a body that plays such a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s intellectual future to operate with such recklessness.
The UTME is a rite of passage for Nigerian students; it should not become a roulette of misfortune. Until JAMB can guarantee a glitch-free, fair, and standardised assessment, its credibility will remain on shaky ground.
In the end, our children deserve better. They deserve an education system that works; not one that breaks down and apologises after the damage is done.
Africa
ECOWAS Confirms Burkina Faso, Mali, Niger’s Exit, Keeps Doors Open for Return

The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) has confirmed that the withdrawal of Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger from the regional bloc takes effect from January 29, 2025.
ECOWAS spokesperson Joel Ahofodji, in a statement on Wednesday, said the decision aligns with the ECOWAS authority’s resolution and reflects the spirit of regional solidarity and the interests of the people.
Despite their exit, Ahofodji emphasized that the bloc remains open to the return of the three Sahel nations whenever they choose.
“All relevant authorities within and outside ECOWAS Member States should take note of this development,” he said.
To minimize disruptions, ECOWAS urged the continued recognition of national passports and identity cards bearing the ECOWAS logo held by citizens of Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger until further notice.
Additionally, the commission called for the continued application of the ECOWAS Trade Liberalisation Scheme (ETLS) and investment policies for goods and services from the departing nations. It also stressed that their citizens should retain the right to visa-free movement, residence, and establishment under existing ECOWAS protocols.
Furthermore, ECOWAS requested full support and cooperation for its officials from the three countries as they continue their assignments.
“These arrangements will be in place until the full determination of the modalities of our future engagement with the three countries by the ECOWAS Authority of Heads of State and Government,” Ahofodji stated.
He revealed that ECOWAS has set up a structure to facilitate discussions on these modalities, ensuring a smooth transition.
“This message is necessary to avoid confusion and disruption in the lives and businesses of our people during this transition period,” he added.
The News Agency of Nigeria (NAN) reports that Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger initially announced their intention to leave ECOWAS on January 29, 2024, in accordance with the bloc’s protocol, which allows for a 12-month notice period. In December 2024, ECOWAS officially acknowledged their right to exit but reiterated its willingness to welcome them back in the future.
Africa
Customs hands over illicit drugs worth N117.59m to NDLEA

The Nigeria Customs Service (NCS), Ogun Area 1 Command, has handed over illicit drugs worth N117.59 million to the National Drug Law Enforcement Agency (NDLEA).
The Comptroller of the command, Mr James Ojo, disclosed this during the handing over of the drugs to Mr Olusegun Adeyeye, the Commander of NDLEA, Idiroko Special Area Command, in Abeokuta, Ogun, on Friday.
Ojo said the customs handed over the seized cannabis and tramadol tablets to the Idiroko Special Command for further investigation in line with the standard operating procedures and inter-agency collaboration.
He said the illicit drugs were seized in various strategic locations between January and November 21, 2024, in Ogun State.
He added that the illicit drugs were abandoned at various locations, including the Abeokuta axis, the Agbawo/Igankoto area of Yewa North Local Government Area, and Imeko Afton axis.
Ojo said that the seizure of the cannabis sativa and tramaling tablets, another brand of tramadol, was made possible through credible intelligence and strategic operations of the customs personnel.
“The successful interception of these dangerous substances would not have been possible without the robust collaboration and support from our intelligence units, local informants and sister agencies.
“These landmark operations are testament to the unwavering dedication of the NCS to safeguard the health and well-being of our citizens and uphold the rule of law,” he said.
He said the seizures comprised 403 sacks and 6,504 parcels, weighing 7,217.7 kg and 362 packs of tramaling tablets of 225mg each, with a total Duty Paid Value of N117,587,405,00.
He described the height of illicit drugs smuggling in the recent time as worrisome.
This, he said, underscores the severity of drug trafficking within the borders.
“Between Oct. 13 and Nov. 12 alone, operatives intercepted a total of 1,373 parcels of cannabis sativa, weighing 1,337kg and 362 packs of tramaling tablets of 225mg each,” he said.
Ojo said the seizures had disrupted the supply chain of illicit drugs, thereby mitigating the risks those substances posed to the youth, families and communities.
He lauded the synergy between its command, security agencies and other stakeholders that led to the remarkable achievements.
Ojo also commended the Comptroller General of NCS for creating an enabling environment for the command to achieve the success.
Responding, Adeyeye, applauded the customs for achieving the feat.
Adeyeye pledged to continue to collaborate with the customs to fight against illicit trade and drug trafficking in the state.
-

 Headlines4 years ago
Headlines4 years agoFacebook, Instagram Temporarily Allow Posts on Ukraine War Calling for Violence Against Invading Russians or Putin’s Death
-
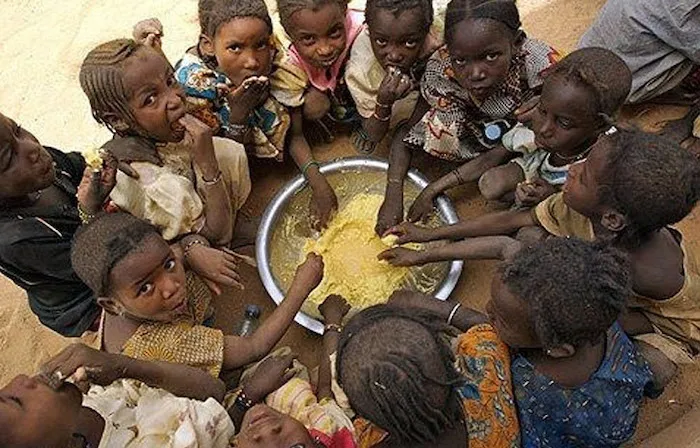

 Headlines4 years ago
Headlines4 years agoNigeria, Other West African Countries Facing Worst Food Crisis in 10 Years, Aid Groups Say
-

 Foreign4 years ago
Foreign4 years agoNew York Consulate installs machines for 10-year passport
-

 News1 year ago
News1 year agoZero Trust Architecture in a Remote World: Securing the New Normal
-
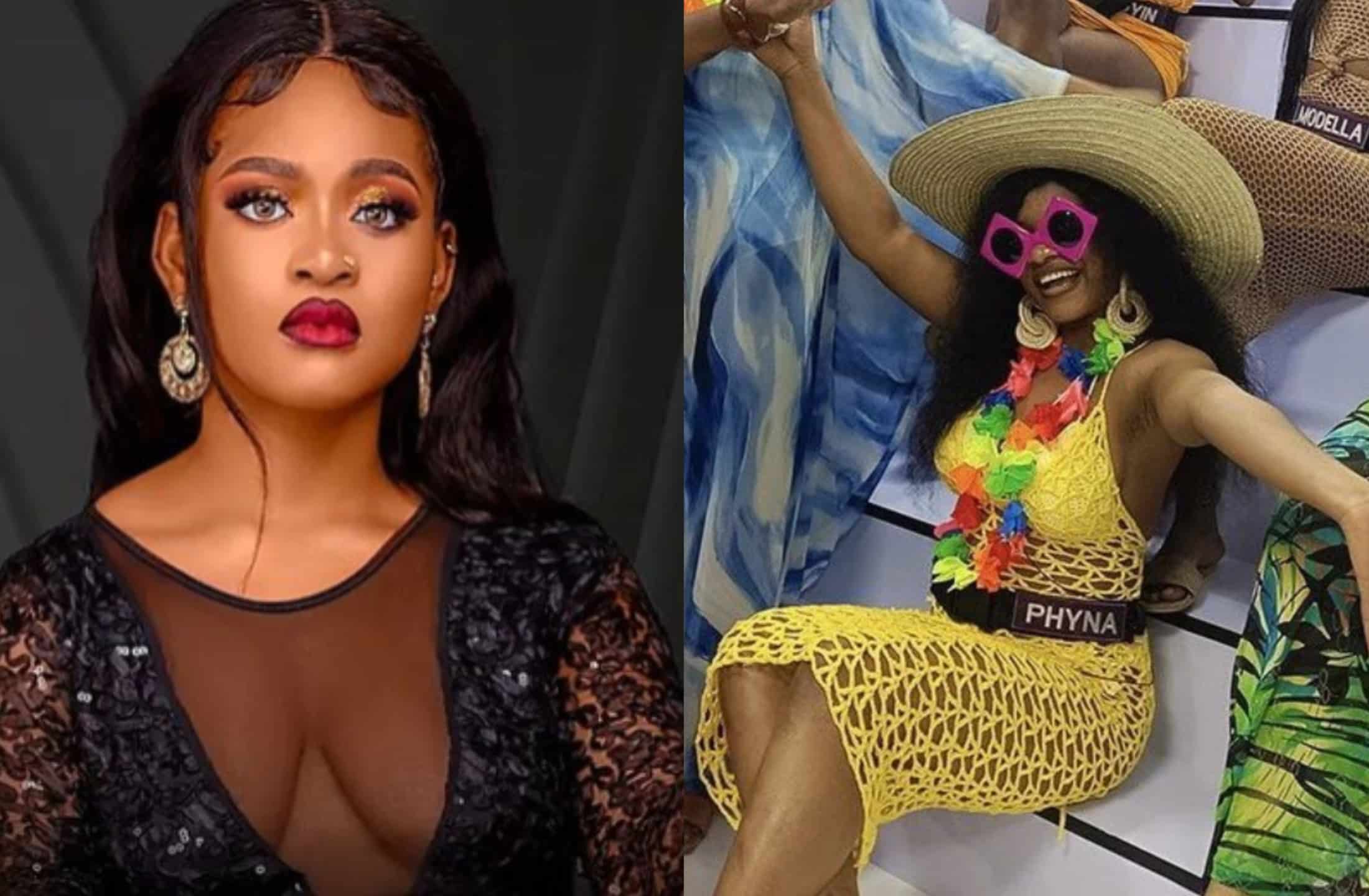

 Entertainment3 years ago
Entertainment3 years agoPhyna emerges winner of Big Brother Naija Season 7
-
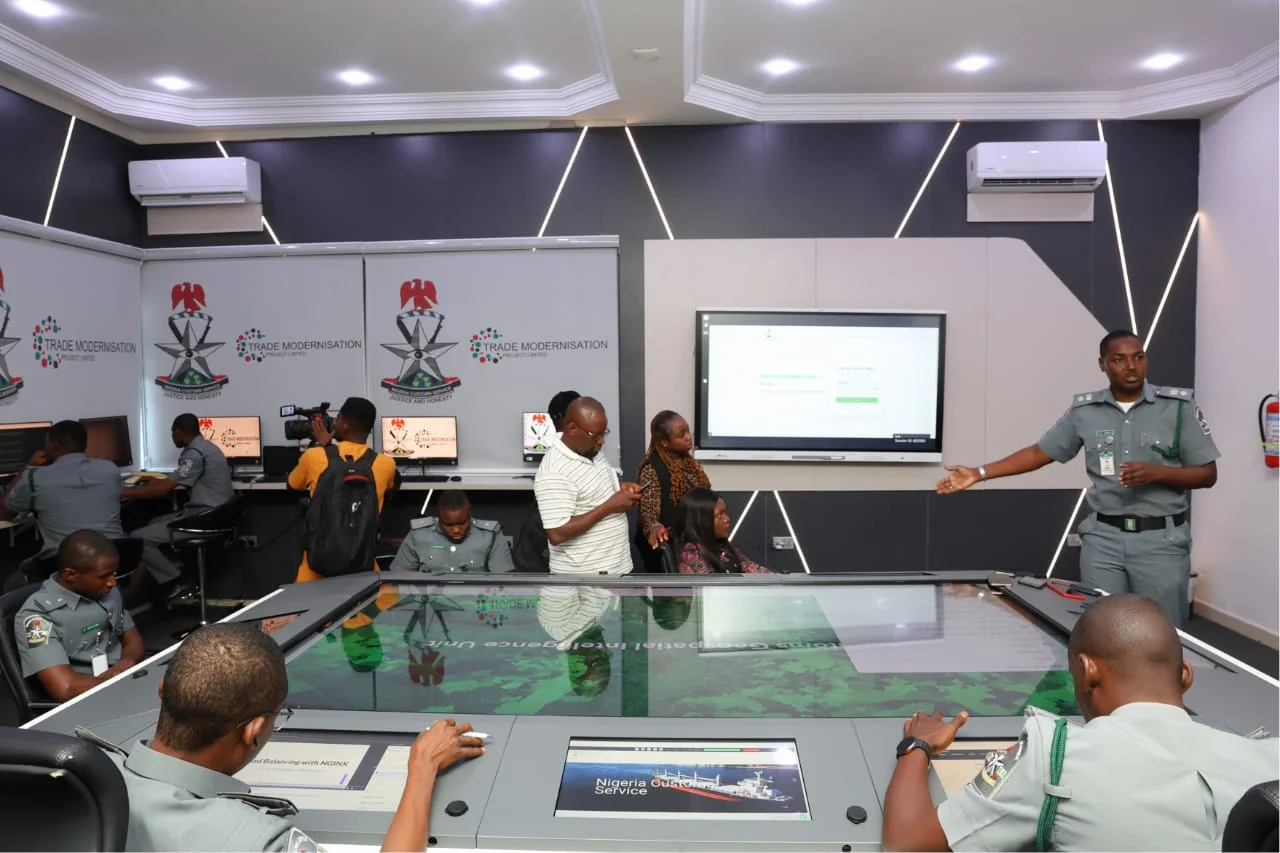

 Headlines2 years ago
Headlines2 years agoNigeria Customs modernisation project to check extortion of traders
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoMovie download platform, Netnaija, announces closure
-

 Economy2 years ago
Economy2 years agoWe generated N30.2 bn revenue in three months – Kano NCS Comptroller